3d shape of enantiomer
Examples of Enantiomers. Another important example of an enantiomer pair is.
Enantiomerism Deranged Physiology
Naproxen S-2-6-methoxy-2-naphthylpropanoic acid is a well-known nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug NSAID and its physiological activity resides in the S enantiomer.

. An example of such an enantiomer is the sedative thalidomide which was sold in a number of countries around the world from 1957 until 1961It was withdrawn from the market when it was. The R-enantiomer fits the active site of a specific enzyme like a key for a specific lock producing the desired sedative effect. The S-enantiomer cannot interact with the same site due.
A left-handed propeller shape left. Imagine looking at the one molecule in the mirror the stereoisomer is its mirror. Enantiomers are mirror images of each other that have a similar molecular shape.
Enantiomers Optical Isomers In three-dimensional 3D space the four covalent bonds of carbon atoms point toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron. Differ in the 3D orientation cistrans enantiomers. In Practical Chemical Thermodynamics for Geoscientists 2013.
The molecules are stereoisomers if they have a different 3D shape and they are not superimposable in space. A basic example of a pair of enantiomers is dextro lactic acid and laevo lactic acid whose chemical structures are given below. Ad Download 100s of 3D Models Graphic Assets Presentations More.
A common example of a pair of enantiomers is dextro lactic acid and laevo lactic acid whose chemical structures are illustrated below. The molecule represented to the right. Enantiomers have a Chiral Carbon.
D Enantiomorphs and enantiomers. It is an enantiomer of a R-adrenaline. In order to draw an enantiomer you can determine the stereocenter then swap the two groups attached to the stereocenter.
An enantiomorph from enantios the Greek word for opposite and morphos the. S-adrenaline is the S-enantiomer of adrenaline. Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable.
Mirror images of molecules. For instance the molecule 1 from above is 1S 2R-2. This simple model was used as an example of how one molecule may be able to fit into the active site of an enzyme but its enantiomer may not.
Enantiomers are a pair of molecules that exist in two forms that can not be superimposed on each other but are mirror images of each other. Diastereomers are non-mirrored images of each other with different molecular shapes. Differ in the way atoms are connected to each other.
Enantiomers refer to isomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another. Orient the molecules so that the green atom points towards each other and the hydrogen atom points up. Each pair of enantiomers have almost identical chemical and physical properties but.
A complex containing three bidentate ligands can take on the shape of a left-handed propeller or a right-handed propeller.
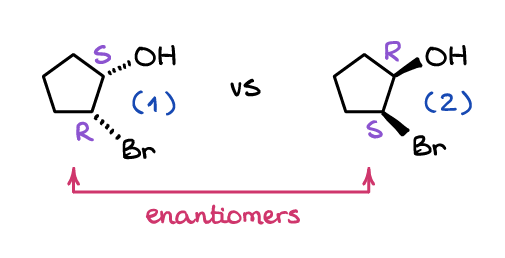
Enantiomers And Diastereomers Organic Chemistry Tutor

Structural Biochemistry Organic Chemistry Stereochemistry Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Enantiomers Of Lactic Acid Download Scientific Diagram
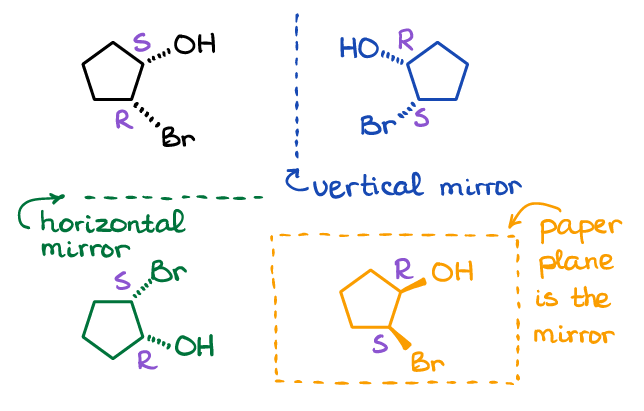
Enantiomers And Diastereomers Organic Chemistry Tutor
How Can We Find Enantiomers Quora

Stereochemistry With 3d Model Superimpose Non Superimpose Enantiomers Mirror Image Youtube

Enantiomers Same But Not Really Stereochemistry
6 3 Optical Activity Chemistry Libretexts

Enantiomers Mirror Image Isomers Youtube

2 21 Carbon Organic Enantiomers Biology Libretexts
Enantiomer 3d Models Sketchfab
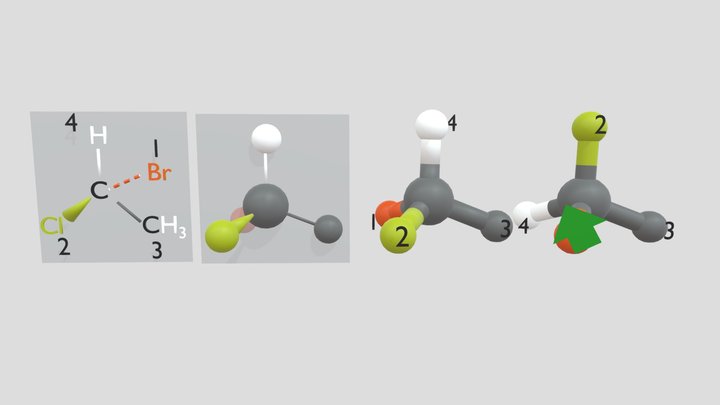
Enantiomer 3d Models Sketchfab

Optical Isomerism Creative Chemistry
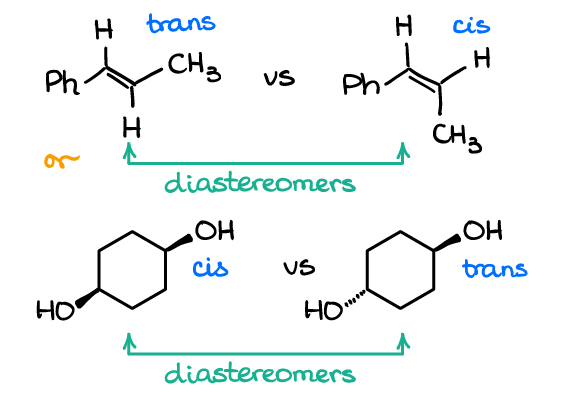
Enantiomers And Diastereomers Organic Chemistry Tutor




